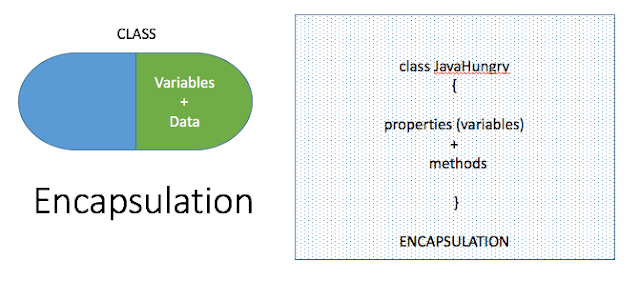
Encapsulation is one of the core concepts of java. In Java, it can be achieved by declaring all variables (data) as a private member and associating these variables with the public get and set methods.
The variables are declared private, the members of other class can’t access the data of encapsulated class directly until the get or set methods are used. Thus, data of encapsulated class are hidden from other classes. Due to this reason, Encapsulation is also called as Data Hiding.
To get in-Depth knowledge on Java you can enroll for a live demo on core Java Online Training
In this concept each member is associated with two kinds of methods:
Setter Method: This method is used to set the value of a private member of the encapsulated class. It takes a value as an argument and assigns that value to the private member. It is written as follows:
public void setMember(datatype value)
{
this.value = value;
}Getter Method: This method returns the value of the private member of the class. It is written as follows:
public datatype getMember()
{
return value;
}Real-Life Example of Encapsulation:
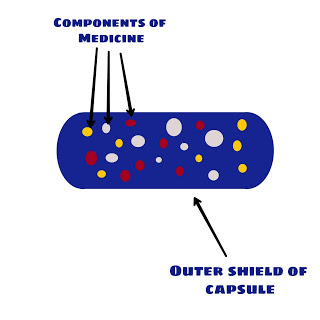
Let’s understand the concept of Encapsulation with the help of a real-life example. For example, consider a Capsule (Medicine). The powder of the capsule consists of various components as well as the outer shield of the capsule protects the internal components from the outer environment. In a similar way, with the help of Encapsulation, we can wrap data and code as a single unit and protect it from outer code.
Take your career to new heights of success with Java Training
General Syntax:
public class JavaHungry
{
private datatype sampleMember1, sampleMember2;
public void setMember1(datatype value)
{
this.sampleMember1 = value;
}
public void setMember2(datatype value)
{
this.sampleMember2 = value;
}
public datatype getMember1()
{
return sampleMember1;
}
public datatype getMember2()
{
return sampleMember2;
}
}The general syntax for encapsulation in Java is shown above. The members of the class are declared private whereas the methods to get and set the values of these members are declared as public. Thus, the outer classes can’t access the members directly instead they have to use these public methods.
Get More Info Java Certification Course
Example for Encapsulation:
//Bank.java (Java file containing Encapsulated Class)
class Bank
{
private String branchName;
private String branchCity;
private int branchPin;
public void setName(String value)
{
this.branchName = value;
}
public void setCity(String value)
{
this.branchCity = value;
}
public void setPin(int value)
{
this.branchPin = value;
}
public String getName()
{
return branchName;
}
public String getCity()
{
return branchCity;
}
public int getPin()
{
return branchPin;
}
}In the above java program, we have created an encapsulated class Bank containing branchName, branchCity, and branchPin as private members. The getter and setter methods are created for each of these private members.
//TestEncapsulate.java (Java File Containing main() method)
public class TestEncapsulate
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String name, city;
int pin;
Bank bank = new Bank();
bank.setName("Sample Bank");
bank.setCity("Sample City");
bank.setPin(100000);
name = bank.getName();
city = bank.getCity();
pin = bank.getPin();
System.out.println("Branch Name: "+name+"\n City: "+city+"\n Pin: "+pin);
}
}Output:
Branch Name: Sample Bank
City: Sample City
Pin: 100000
Advantages of Encapsulation:
1. Data Hiding: Encapsulation provides a protective shield to the members of a class and prevents it from the outer code. The user will not know how and where the data is being stored. Users will be unaware of the inner implementation of the class. Therefore Encapsulation provides the facility of Data Hiding from outer classes and users.
2. Flexibility: Encapsulation creates the code more flexible. There is no need to worry about how and where to store data as well as how to access them because getter and setter methods do these functionalities.
3. Reusability: The code becomes more useable as it’s easy to change the encapsulated class with the change of requirements.