Java has several classes in its components. In this article, I would like to mention java scanner class. The java scanner class consists of following
- Java scanner class
- Class constructors
- Java scanner class modifier
So first let us see in brief about Java scanner class.
To get in-Depth knowledge on Java you can enroll for a live demo on Java Online Training
Java scanner class:
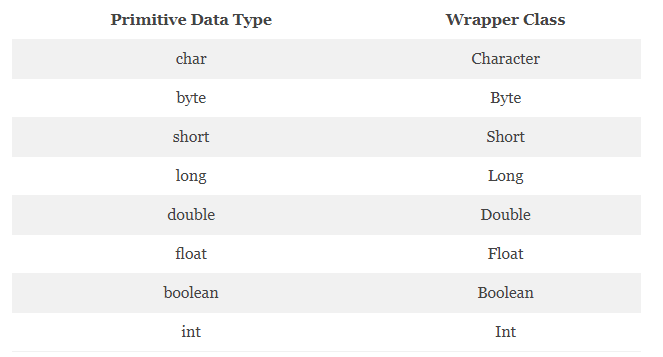
Java Scanner Class is a class in java.util package that uses primitive types such as int, double, etc., and strings to get data. Reading input in a Java program is the simplest way.
Typically we transfer the predefined object System.in, which represents the default input stream, to build a Scanner class object. If we want to read input from a file, we can transfer an object in class File.
The feature to use is nextXYZ()for reading numerical values of a given data form XYZ. For example, we can use nextShort()To read strings, we use nextLine()to read a short type value.
Take your career to new heights of success with Java Training
We use next charAt(0), to read a single character. If you want to return to next character in the string use next() function, the next token or word in the input string and to return first character we use charat()The Java scanner class has the following components
- Class constructors
- modifiers
Class constructor in java:
These are several class constructors in java scanner class.
- Scanner(File source)
Builds a new Scanner which produces scanned values from the specified file.
- Scanner(File source, String charsetName)
Constructs a new Scanner which generates scanned values from the specified file.
- Scanner(InputStream source)
Builds a new Scanner which produces scanned values from the specified input stream.
- Scanner(InputStream source, String charsetName)
Constructs a new Scanner which produces scanned values from the specified input stream.
- Scanner(Readable source)
Constructs a new Scanner which produces scanned values from the specified source.
- Scanner(String source)
It Creates a new Scanner that produces scanned values from the given Java string.
- Scanner(ReadableByteChannel source)
It Creates a new Scanner that generates values scanned from the channel specified.
- Scanner(ReadableByteChannel source, String charsetName)
Builds a new Scanner that produces values scanned from the channel in question.
- Scanner(Path source)
Builds a new Scanner which produces scanned values from the specified file.
- Scanner(Path source, String charsetName)
Constructs a new Scanner which generates scanned values from the specified file.
Java scanner class methods:
The following are java methods. I listed out the modifiers and the method of using it
To learn more about Java scanner class and other great features of Java, you can enroll for a live demo on Core Java Online Training
Vacuum
Method: close()
We use this scanner to close.
Pattern
Method: delimiter()
We use the pattern that the Scanner class actually uses to suit boundaries to get it.
Stream
Method: < MatchResult > findAll()
We use it to find a match string matching the specified pattern list.
String
Method: findInLine()
We use it to find the next occurrence of a pattern constructed from the specified string, ignoring boundaries.
String find
Method: WithinHorizon()
We use it to detect the next occurrence of a pattern constructed from the specified string, ignoring boundaries.
Boolean
Method: hasNext()
If this scanner has a different token in its input, it will return valid.
Boolean
Method: NextBigDecimal()
We use it to test whether or not the next token in the input of that scanner can be interpreted as BigDecimal using the nextBigDecimal()process.
Boolean
Method: NextBigInteger()
It Checks whether or not the next token in the input of this scanner can be interpreted as a BigDecimal using the nextBigDecimal()process.
Boolean
Method: NextBoolean()
We use it to test whether or not the next token in the input of the scanner can be interpreted as Boolean using the nextBoolean()process.
Boolean
Method: NextByte()
We use it to check whether or not the next token in the input of this scanner can be interpreted as a Byte using the nextBigDecimal()process.
Boolean
Method: NextDouble()
We use it to test whether or not the next token in the input of that scanner can be interpreted as BigDecimal using the nextByte()method.
Boolean
Method: NextFloat()
It Checks whether or not the next token in the input of this scanner can be interpreted as a Float using the nextFloat()form.
Boolean
Method: NextInt()
We use it to evaluate whether or not the next token in the input of this scanner can be interpreted as an int using the nextInt()process.
Boolean
Method: NextLine()
We use it to verify if the input of this scanner has a different line or not.
Boolean
Method: NextLong()
We use it to test whether or not the next token in the input of the scanner can be interpreted as a Long using the nextLong()process.
Boolean
Method: NextShort()
We use it to test whether or not the next token in the input of the scanner can be interpreted as a Short using the nextShort()process.
IOException
Method: ioException()
We use it to get the last thrown IOException readable by this Scanner.
Local locale()
Method: We use it to get a Scanner class Local.
MatchResult
Method: match()
The result of the last scanning operation performed by this scanner is used to get match.
String
Method: next()
We use it to get the next complete token from the scanner you are using.
BigDecimal
Method: nextBigDecimal()
It Scans the BigDecimal token next to the data.
BigInteger
Method: nextBigInteger()
It Checks the next input token as a BigInteger.
Boolean
Method: nextBoolean()
It Scans the next input token into a boolean value, returning the value.
Byte
Method: nextByte()
It Checks the next input token as byte.
Double
Method: nextDouble()
It Scans the next input token as double.
Float
Method: nextFloat()
It Checks the next input token like a float.
int
Method: nextInt()
It Scans the next Input token as an Int.
String
Method: nextLine()
The input string which was skipped from the Scanner object is used to get.
Long
Method: nextLong()
It Scans the next input token as long.
Short
Method: nextShort()
It Scans the next input token as short.
int
Method: radix()
The default radix for use with the Scanner is used.
Void
Method: remove()
We use it when this Iterator implementation does not support the remove operation.
Reset()
We use Scanner to reset the Scanner currently in use.
Scanner
Method: skip()
It Skips input that fits the specified sequence, ignoring boundaries
Stream
Method: < String > tokens()
We use it to get a delimiter-separated tokens stream from the Scanner object being used.
String
Method: toString()
It is for using the Scanner string representation.
Use
Method: Delimiter()
Scanner is used to set the Scanner bonding pattern in use to the specified pattern.
Use
Method: Locale()
Scanner to set the locale object of this scanner to the specified locale.
Scanner
Method: useRadix()
We use The default Scanner radix for the specified radix.
Example for java scanner class:
Let us see a simple example program for java scanner class.
import java.util.*;
public class ScannerExample {
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter your name: ");
String name = in.nextLine();
System.out.println("Name is: " + name);
in.close();
}
}
By running this program in the compiler you get output of entered name.
Conclusion:
I hope you reach a conclusion about the Java Scanner class by reading this article. You can learn more about Java scanner class, constructor classes, modifiers through Java online training from industry experts.